Temporary and Permanent Services for Construction Power
Information Bulletin
Information Bulletin: Temporary and Permanent Services for Construction Power
March 4, 2025
Reference Number:
IB-EL 2016-03
Revision Number:
Revision 3
This bulletin provides guidance on the application of rules outlined in the 2024 BC Electrical Code. The requirements may vary depending on the local municipal authorities that have jurisdiction. Installers should consult with local authorities that hold jurisdiction before starting work to determine their requirements.
A: Temporary Services and Wiring for Buildings Under Construction or Demolition
1. Scope
As outlined in rule 76-000 of the BC Electrical Code, Section 76 applies to temporary wiring installations for buildings under construction or demolition. It is the nature of the installation, not the use of that installation, that determines whether the installation is temporary. Receptacles that are connected to the permanent wiring system and therefore not within the scope of section 76 are subject to other applicable rules of the BC Electrical Code. Temporary distribution panels are not considered permanent and are subject to the rules in section 76.
2. Receptacles
Construction sites using temporary wiring methods should be aware that this wiring is exposed to more severe duty and weather conditions than permanent installations. The use of extension cords may increase bonding conductor impedance. Additionally, site and environmental conditions may make grounding conditions unstable. These factors can result in a higher risk of electrical shock to workers. For this reason, rule 76-016 requires GFCI protection for 15amp configuration (5-15R) and 20amp configuration (5-20R) receptacles installed for temporary wiring installations. See also BC Electrical code Rule 26-708 Receptacles exposed to the weather.
3. Electrical Temporary Construction Operating Permit Requirements
A temporary operating permit is required for service installations that are temporary in nature and will be disconnected once the construction or demolition phase of work is completed. In many cases, the contractor installing the equipment may not be the same contractor or Field Safety Representative (FSR) who monitors ongoing safety for operation and maintenance of the equipment. The temporary operating permit authorizes installation of the equipment, and the permit holder is responsible for ensuring a field safety representative monitors the ongoing safe operation and maintenance of the equipment for the duration of its operation. The temporary operating permit must be obtained by the equipment owner. An “owner” may be the lessee as defined in the Safety Standards Act. The permit holder must name a Field Safety Representative on the permit.
The temporary operating permit is valid for 12 months from the date of issue. This permit is not renewable. A new, temporary construction operating permit must be obtained after 12 months if the temporary service is still required. To complete the temporary construction operating permit, the temporary construction service must be disconnected from the electrical supply before submitting a request for a Final – “All Work is Complete” inspection request.
4. Temporary Construction Services (Pole Mount 200 Amps or Less)
Temporary construction service installations will be accepted if they have been constructed in accordance with attached diagrams 1-2 and have satisfied the following requirements:
- Be protected from the weather and mechanical damage by location or by installing the equipment within an enclosure that has been made weatherproof, or by using a Type 3R weatherproof enclosure, and
- The equipment must be capable of being locked, and
- All panel covers must be installed while the equipment was energized, and
- Receptacles supplying temporary power for construction purposes must comply with the requirements of rules 76-016, (26-708) and
- Branch circuits must comply with the requirements of rule 76-012. (and/ or 12-100)
- Device, junction and outlet boxes to comply with 2-400.
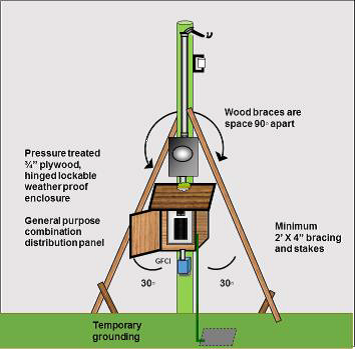 DIAGRAM 1
|
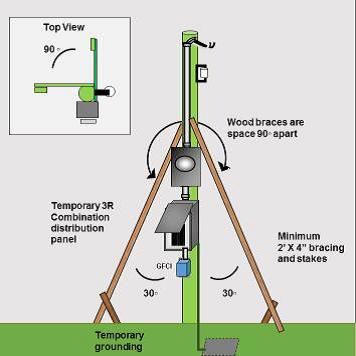 DIAGRAM 2
|
B: Permanent Services and Wiring for Buildings Under Construction
1. Electrical service equipment such as panel boards and circuit breakers installed during construction to provide temporary power must be installed to ensure the electrical equipment is not exposed to moisture or damage during the construction phase.
2. Permanently installed receptacles do not require GFCI protection even though they may be energized for use during construction. All receptacles in outdoor locations must be weather protected as required in rule 26-708. All receptacles having CSA configuration 5-15R or 5-20R, installed outdoors and within 2.5 m of finished grade, shall be protected with a ground fault circuit interrupter of the Class A type as per 26-704 2).
Permanent construction service installations will be accepted if they are constructed in accordance with attached diagrams 3 - 8 and satisfy the following requirements:
- Be protected from the weather and mechanical damage by location, by installing the equipment within a weatherproof enclosure, or by using a Type 3R enclosure, and
- The electrical service equipment must be capable of being locked, if the building is not to the lock-up stage (i.e., lockable windows and doors installed), and
- All panel covers must be installed while the equipment is energized, and
- Receptacles and branch circuits supplying temporary power for construction purposes must comply with the requirements of section 76; and
- Receptacles and branch circuits that form part of the permanent wiring, but are used for the construction phase must comply with the general sections of the code, and
- Receptacles exposed to weather must comply with rule 26-708.
- Device boxes exposed to weather must comply with rule 2-400.
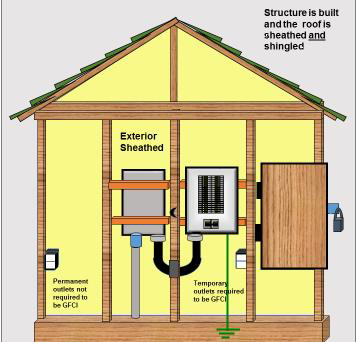 DIAGRAM 3 Enclosed building (not at lock-up stage) with roofing material installed:
|
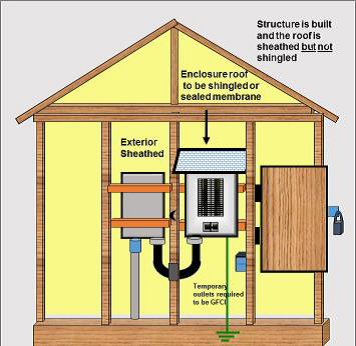 DIAGRAM 4 Enclosed building (not at lock-up stage) with roofing material not installed:
|
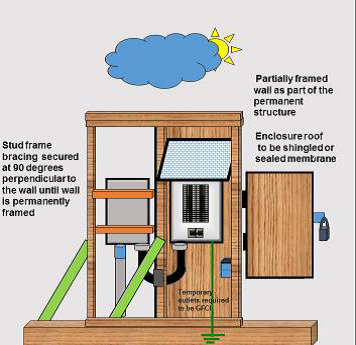 DIAGRAM 5 Open structure exposed to weather (front view):
|
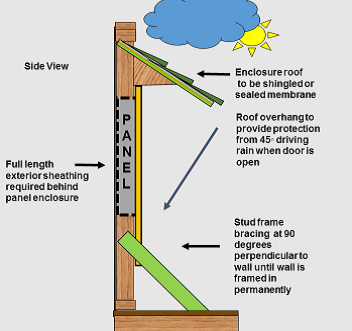 DIAGRAM 6 Open structure exposed to weather (side view):
NOTE: Enclosure roof overhang to extend forward sufficiently to protect service equipment (when door open) from 45◦ driving rain |
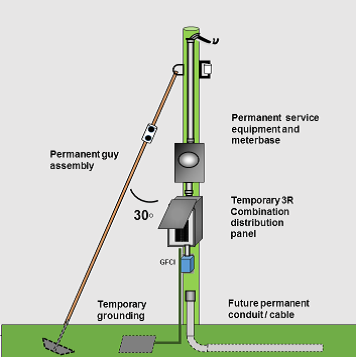 DIAGRAM 7 Permanent service pole and meter base – temporary distribution panel:
|
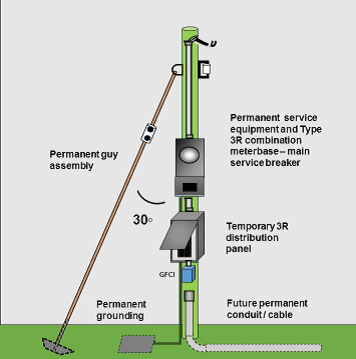 DIAGRAM 8 Permanent service pole and combination meter base / main service breaker – temporary distribution panel:
|
Vicky Kang
Manager, Energy
Provincial Safety Manager, Electrical
References:
Safety Standards Act
Electrical Safety Regulation
Safety Standards General Regulation